Archives of Disease in Childhood, 2023
Obesity and excess adiposity are leading causes of metabolic and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Early identification of individuals at risk is key for preventive strategies. We examined the relationship between infant body composition (0–2 years of age) and later (>2 years) health outcomes using a systematic review.
European Journal of Nutrition , 2022
To summarize current knowledge and gaps regarding the role of postprandial glycaemic response in the paediatric population, a workshop was organized in June 2021 by the European branch of the International Life Science Institute (ILSI). The workshop led to the consensus on the crucial role on health of postprandial glycaemic response in paediatric population.
Beneficial Microbes, 2022
he intestinal microbiota plays a major role in infant health and development. However, the role of the breastmilk microbiota in infant gut colonisation remains unclear. A systematic review was performed to evaluate the composition of the breastmilk microbiota and evidence for transfer to/colonisation of the infant gut
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences, 2022
(2022) 79:80. Commissioned by the Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health, Nutrition and Brain Health, Nutrition, Immunity and Inflammation, Prebiotics and Probiotics Task Forces.
Critical Reviews in Microbiology 2020. Commissioned by the Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health Task Force.
WP_Query Object
(
[query] => Array
(
[post_type] => publication
[posts_per_page] => 5
[type] =>
[area] =>
[committee] => Metabolic Imprinting
[authors] =>
[showtitle] =>
[meta_query] => Array
(
[relation] => AND
)
[tax_query] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[taxonomy] => ilsi_committee
[field] => name
[terms] => Metabolic Imprinting
)
)
[paged] => 1
[meta_key] => _ilsi_date
[orderby] => meta_value
[order] => DESC
)
[query_vars] => Array
(
[post_type] => publication
[posts_per_page] => 5
[type] =>
[area] =>
[committee] => Metabolic Imprinting
[authors] =>
[showtitle] =>
[meta_query] => Array
(
[relation] => AND
)
[tax_query] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[taxonomy] => ilsi_committee
[field] => name
[terms] => Metabolic Imprinting
)
)
[paged] => 1
[meta_key] => _ilsi_date
[orderby] => meta_value
[order] => DESC
[error] =>
[m] =>
[p] => 0
[post_parent] =>
[subpost] =>
[subpost_id] =>
[attachment] =>
[attachment_id] => 0
[name] =>
[pagename] =>
[page_id] => 0
[second] =>
[minute] =>
[hour] =>
[day] => 0
[monthnum] => 0
[year] => 0
[w] => 0
[category_name] =>
[tag] =>
[cat] =>
[tag_id] =>
[author] =>
[author_name] =>
[feed] =>
[tb] =>
[meta_value] =>
[preview] =>
[s] =>
[sentence] =>
[title] =>
[fields] =>
[menu_order] =>
=>
[category__in] => Array
(
)
[category__not_in] => Array
(
)
[category__and] => Array
(
)
[post__in] => Array
(
)
[post__not_in] => Array
(
)
[post_name__in] => Array
(
)
[tag__in] => Array
(
)
[tag__not_in] => Array
(
)
[tag__and] => Array
(
)
[tag_slug__in] => Array
(
)
[tag_slug__and] => Array
(
)
[post_parent__in] => Array
(
)
[post_parent__not_in] => Array
(
)
[author__in] => Array
(
)
[author__not_in] => Array
(
)
[search_columns] => Array
(
)
[ignore_sticky_posts] =>
[suppress_filters] =>
[cache_results] => 1
[update_post_term_cache] => 1
[update_menu_item_cache] =>
[lazy_load_term_meta] => 1
[update_post_meta_cache] => 1
[nopaging] =>
[comments_per_page] => 50
[no_found_rows] =>
[taxonomy] => ilsi_committee
[term_id] => Metabolic Imprinting
)
[tax_query] => WP_Tax_Query Object
(
[queries] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[taxonomy] => ilsi_committee
[terms] => Array
(
[0] => Metabolic Imprinting
)
[field] => name
[operator] => IN
[include_children] => 1
)
)
[relation] => AND
[table_aliases:protected] => Array
(
[0] => wp_3_term_relationships
)
[queried_terms] => Array
(
[ilsi_committee] => Array
(
[terms] => Array
(
[0] => Metabolic Imprinting
)
[field] => name
)
)
[primary_table] => wp_3_posts
[primary_id_column] => ID
)
[meta_query] => WP_Meta_Query Object
(
[queries] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_date
)
[relation] => OR
)
[relation] => AND
[meta_table] => wp_3_postmeta
[meta_id_column] => post_id
[primary_table] => wp_3_posts
[primary_id_column] => ID
[table_aliases:protected] => Array
(
[0] => wp_3_postmeta
)
[clauses:protected] => Array
(
[wp_3_postmeta] => Array
(
[key] => _ilsi_date
[compare] => =
[compare_key] => =
[alias] => wp_3_postmeta
[cast] => CHAR
)
)
[has_or_relation:protected] =>
)
[date_query] =>
[request] =>
SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS wp_3_posts.ID
FROM wp_3_posts LEFT JOIN wp_3_term_relationships ON (wp_3_posts.ID = wp_3_term_relationships.object_id) INNER JOIN wp_3_postmeta ON ( wp_3_posts.ID = wp_3_postmeta.post_id )
WHERE 1=1 AND (
wp_3_term_relationships.term_taxonomy_id IN (26)
) AND (
wp_3_postmeta.meta_key = '_ilsi_date'
) AND ((wp_3_posts.post_type = 'publication' AND (wp_3_posts.post_status = 'publish' OR wp_3_posts.post_status = 'acf-disabled')))
GROUP BY wp_3_posts.ID
ORDER BY wp_3_postmeta.meta_value DESC
LIMIT 0, 5
[posts] => Array
(
[0] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 13987
[post_author] => 351
[post_date] => 2023-11-09 08:52:48
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-11-09 08:52:48
[post_content] =>
Objective
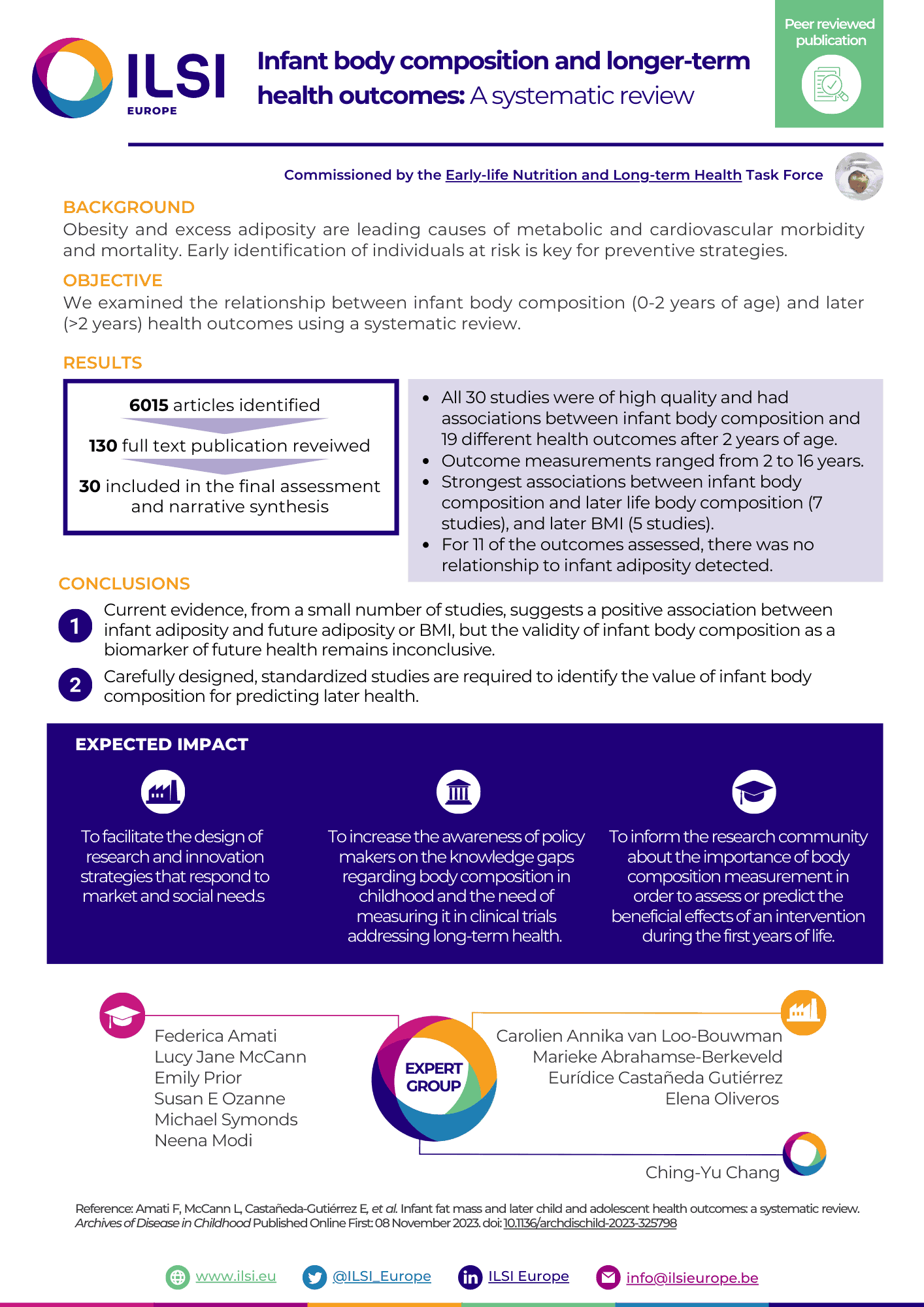
Obesity and excess adiposity are leading causes of metabolic and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Early identification of individuals at risk is key for preventive strategies. We examined the relationship between infant body composition (0-2 years of age) and later (>2 years) health outcomes using a systematic review.
Design
We preregistered the study on PROSPERO (ID 288013) and searched Embase, PubMed and Cochrane databases for English language publications using the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms 'infant' and 'body composition' and 'risk' between January 1946 and February 2022. We included studies which assessed infant body composition using predetermined in vivo methods other than body mass index (BMI).
Results
We identified 6015 articles. After abstract screening to assess eligibility, we reviewed 130 full text publications. 30 were included in the final assessment and narrative synthesis. Meta-analysis was not possible due to heterogeneity of results. All 30 studies were of high quality and reported associations between infant body composition and 19 different health outcomes after 2 years of age. Outcome measurements ranged from 2 years to 16 years. The strongest associations were found between infant fat mass and later fat mass (7 studies), and later BMI (5 studies). For 11 of the outcomes assessed, there was no relationship to infant adiposity detected.
Conclusions
Current evidence, from a small number of studies, suggests a positive association between infant adiposity and future adiposity or BMI, but the validity of infant body composition as a biomarker of future health remains inconclusive. Carefully designed, standardised studies are required to identify the value of infant body composition for predicting later health.
Download the full article here.
Download the article one-pager below
 [post_title] => Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=13987
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[1] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 12345
[post_author] => 24
[post_date] => 2023-01-04 12:00:18
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-01-04 12:00:18
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Health relevance of lowering postprandial glycaemia in the paediatric population through diet’: results from a multistakeholder workshop
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => health-relevance-of-lowering-postprandial-glycaemia-in-the-paediatric-population-through-diet-results-from-a-multistakeholder-workshop
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-06-19 12:46:23
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-06-19 12:46:23
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=12345
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[2] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 12225
[post_author] => 24
[post_date] => 2022-11-15 14:24:37
[post_date_gmt] => 2022-11-15 14:24:37
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=13987
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[1] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 12345
[post_author] => 24
[post_date] => 2023-01-04 12:00:18
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-01-04 12:00:18
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Health relevance of lowering postprandial glycaemia in the paediatric population through diet’: results from a multistakeholder workshop
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => health-relevance-of-lowering-postprandial-glycaemia-in-the-paediatric-population-through-diet-results-from-a-multistakeholder-workshop
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-06-19 12:46:23
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-06-19 12:46:23
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=12345
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[2] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 12225
[post_author] => 24
[post_date] => 2022-11-15 14:24:37
[post_date_gmt] => 2022-11-15 14:24:37
[post_content] =>
The intestinal microbiota plays a major role in infant health and development. However, the role of the breastmilk microbiota in infant gut colonisation remains unclear. A systematic review was performed to evaluate the composition of the breastmilk microbiota and evidence for transfer to/colonisation of the infant gut. Searches were performed using PUBMED, OVID, LILACS and PROQUEST from inception until 18th March 2020 with a PUBMED update to December 2021. 88 full texts were evaluated before final critique based on study power, sample contamination avoidance, storage, purification process, DNA extraction/analysis, and consideration of maternal health and other potential confounders. Risk of skin contamination was reduced mainly by breast cleaning and rejecting the first milk drops. Sample storage, DNA extraction and bioinformatics varied. Several studies stored samples under conditions that may selectively impact bacterial DNA preservation, others used preculture reducing reliability. Only 15 studies, with acceptable sample size, handling, extraction, and bacterial analysis, considered transfer of bacteria to the infant. Three reported bacterial transfer from infant to breastmilk. Despite consistent evidence for the breastmilk microbiota, and recent studies using improved methods to investigate factors affecting its composition, few studies adequately considered transfer to the infant gut providing very little evidence for effective impact on gut colonisation.
Keywords
Expand
Microbiota, infant, breast milk, gut colonisation, systematic review
To download this open-access article, please click here.
Commissioned by the Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health Task Force.
[post_title] => A systematic review of breast milk microbiota composition and the evidence for transfer to and colonisation of the infant gut
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => a-systematic-review-of-breast-milk-microbiota-composition-and-the-evidence-for-transfer-to-and-colonisation-of-the-infant-gut
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2023-06-19 12:47:12
[post_modified_gmt] => 2023-06-19 12:47:12
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=12225
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[3] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 10456
[post_author] => 24
[post_date] => 2022-03-28 13:12:46
[post_date_gmt] => 2022-03-28 13:12:46
[post_content] =>
GUT MICROBIOME AND HEALTH and NUTRITION AND CONSUMER SCIENCE
The gut and brain link via various metabolic and signalling pathways, each with the potential to influence mental, brain and cognitive health. Over the past decade, the involvement of the gut microbiota in gut-brain communication has become the focus of increased scientific interest, establishing the microbiota-gut-brain axis as a field of research. There is a growing number of association studies exploring the gut microbiota's possible role in memory, learning, anxiety, stress, neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders. Consequently, attention is now turning to how the microbiota can become the target of nutritional and therapeutic strategies for improved brain health and well-being. However, while such strategies that target the gut microbiota to influence brain health and function are currently under development with varying levels of success, still very little is yet known about the triggers and mechanisms underlying the gut microbiota's apparent influence on cognitive or brain function and most evidence comes from pre-clinical studies rather than well controlled clinical trials/investigations. Filling the knowledge gaps requires establishing a standardised methodology for human studies, including strong guidance for specific focus areas of the microbiota-gut-brain axis, the need for more extensive biological sample analyses, and identification of relevant biomarkers. Other urgent requirements are new advanced models for in vitro and in vivo studies of relevant mechanisms, and a greater focus on omics technologies with supporting bioinformatics resources (training, tools) to efficiently translate study findings, as well as the identification of relevant targets in study populations. The key to building a validated evidence base rely on increasing knowledge sharing and multi-disciplinary collaborations, along with continued public-private funding support. This will allow microbiota-gut-brain axis research to move to its next phase so we can identify realistic opportunities to modulate the microbiota for better brain health.
To download this open-access article, please click here.
This work was conducted in collaboration with the Early Nutrition and Long-Term Health, Nutrition and Brain Health, Nutrition, Immunity and Inflammation, Prebiotics and Probiotics Task Forces.
[post_title] => The microbiota–gut–brain axis: pathways to better brain health. Perspectives on what we know, what we need to investigate and how to put knowledge into practice
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => the-microbiota-gut-brain-axis-pathways-to-better-brain-health-perspectives-on-what-we-know-what-we-need-to-investigate-and-how-to-put-knowledge-into-practice
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2022-10-10 06:51:51
[post_modified_gmt] => 2022-10-10 06:51:51
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=10456
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[4] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 8022
[post_author] => 204
[post_date] => 2020-09-16 14:16:43
[post_date_gmt] => 2020-09-16 14:16:43
[post_content] =>
[post_title] => Is there Evidence for Bacterial Transfer via the Placenta and any Role in the Colonization of the Infant Gut? – a Systematic Review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => is-there-evidence-for-bacterial-transfer-via-the-placenta-and-any-role-in-the-colonization-of-the-infant-gut-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2020-09-16 14:18:42
[post_modified_gmt] => 2020-09-16 14:18:42
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=8022
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
)
[post_count] => 5
[current_post] => -1
[before_loop] =>
[in_the_loop] =>
[post] => WP_Post Object
(
[ID] => 13987
[post_author] => 351
[post_date] => 2023-11-09 08:52:48
[post_date_gmt] => 2023-11-09 08:52:48
[post_content] =>
Objective
Obesity and excess adiposity are leading causes of metabolic and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Early identification of individuals at risk is key for preventive strategies. We examined the relationship between infant body composition (0-2 years of age) and later (>2 years) health outcomes using a systematic review.
Design
We preregistered the study on PROSPERO (ID 288013) and searched Embase, PubMed and Cochrane databases for English language publications using the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms 'infant' and 'body composition' and 'risk' between January 1946 and February 2022. We included studies which assessed infant body composition using predetermined in vivo methods other than body mass index (BMI).
Results
We identified 6015 articles. After abstract screening to assess eligibility, we reviewed 130 full text publications. 30 were included in the final assessment and narrative synthesis. Meta-analysis was not possible due to heterogeneity of results. All 30 studies were of high quality and reported associations between infant body composition and 19 different health outcomes after 2 years of age. Outcome measurements ranged from 2 years to 16 years. The strongest associations were found between infant fat mass and later fat mass (7 studies), and later BMI (5 studies). For 11 of the outcomes assessed, there was no relationship to infant adiposity detected.
Conclusions
Current evidence, from a small number of studies, suggests a positive association between infant adiposity and future adiposity or BMI, but the validity of infant body composition as a biomarker of future health remains inconclusive. Carefully designed, standardised studies are required to identify the value of infant body composition for predicting later health.
Download the full article here.
Download the article one-pager below
 [post_title] => Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=13987
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[comment_count] => 0
[current_comment] => -1
[found_posts] => 12
[max_num_pages] => 3
[max_num_comment_pages] => 0
[is_single] =>
[is_preview] =>
[is_page] =>
[is_archive] => 1
[is_date] =>
[is_year] =>
[is_month] =>
[is_day] =>
[is_time] =>
[is_author] =>
[is_category] =>
[is_tag] =>
[is_tax] => 1
[is_search] =>
[is_feed] =>
[is_comment_feed] =>
[is_trackback] =>
[is_home] =>
[is_privacy_policy] =>
[is_404] =>
[is_embed] =>
[is_paged] =>
[is_admin] =>
[is_attachment] =>
[is_singular] =>
[is_robots] =>
[is_favicon] =>
[is_posts_page] =>
[is_post_type_archive] =>
[query_vars_hash:WP_Query:private] => 092dab48ffb1b3d56c63b40a510c67fc
[query_vars_changed:WP_Query:private] =>
[thumbnails_cached] =>
[allow_query_attachment_by_filename:protected] =>
[stopwords:WP_Query:private] =>
[compat_fields:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => query_vars_hash
[1] => query_vars_changed
)
[compat_methods:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => init_query_flags
[1] => parse_tax_query
)
)
[post_title] => Infant fat mass and later child and adolescent health outcomes: a systematic review
[post_excerpt] =>
[post_status] => publish
[comment_status] => closed
[ping_status] => closed
[post_password] =>
[post_name] => infant-fat-mass-and-later-child-and-adolescent-health-outcomes-a-systematic-review
[to_ping] =>
[pinged] =>
[post_modified] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_modified_gmt] => 2024-03-15 15:13:16
[post_content_filtered] =>
[post_parent] => 0
[guid] => https://ilsi.eu/?post_type=publication&p=13987
[menu_order] => 0
[post_type] => publication
[post_mime_type] =>
[comment_count] => 0
[filter] => raw
)
[comment_count] => 0
[current_comment] => -1
[found_posts] => 12
[max_num_pages] => 3
[max_num_comment_pages] => 0
[is_single] =>
[is_preview] =>
[is_page] =>
[is_archive] => 1
[is_date] =>
[is_year] =>
[is_month] =>
[is_day] =>
[is_time] =>
[is_author] =>
[is_category] =>
[is_tag] =>
[is_tax] => 1
[is_search] =>
[is_feed] =>
[is_comment_feed] =>
[is_trackback] =>
[is_home] =>
[is_privacy_policy] =>
[is_404] =>
[is_embed] =>
[is_paged] =>
[is_admin] =>
[is_attachment] =>
[is_singular] =>
[is_robots] =>
[is_favicon] =>
[is_posts_page] =>
[is_post_type_archive] =>
[query_vars_hash:WP_Query:private] => 092dab48ffb1b3d56c63b40a510c67fc
[query_vars_changed:WP_Query:private] =>
[thumbnails_cached] =>
[allow_query_attachment_by_filename:protected] =>
[stopwords:WP_Query:private] =>
[compat_fields:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => query_vars_hash
[1] => query_vars_changed
)
[compat_methods:WP_Query:private] => Array
(
[0] => init_query_flags
[1] => parse_tax_query
)
)


